Machine designers needing a high-precision linear guide usually have little choice except higher-cost profile rail, but within this component’s realm, diligent analysis can keep those costs to a minimum. Too often, however, in the press of project deadlines, designers may not have the time to conduct the necessary analysis to map rail functionalities to their application needs and end up paying a premium for impractical features. Plus, the larger the production run, the greater the potential problems.

What drives profile rail costs?
The primary cost factors in profile rail selection are essentially prescribed by the motion profile, but there are other areas where the design has more leeway to manage trade-offs. The selection of ball track assemblies can make a huge difference in the cost. Other factors, including material selection, maintenance, standards compliance, and training offer additional opportunities for cost reduction, albeit with varying degrees of influence on upfront versus long-term expenses.
Cost-optimizing ball track position
How the machine designer wants to position load-carrying and contacting elements in relation to each other significantly impacts cost. The three most common options are a double-faced arrangement with spherical balls, a double-backed arrangement with spherical balls and a double-backed arrangement with rollers.
Double-faced ball tracks
A double-faced ball-track arrangement is the least expensive. It arranges ball tracks with contact angles at 45 degrees, causing an X pattern. (Figure 1) The X-type configuration optimizes the distribution of load across all the rolling elements, enabling convergence of force vectors close to the center of rotation. Centralizing the force vectors in this way makes the double-faced arrangement much more tolerant of misalignment and mounting surface imperfection, significantly reducing installation and mounting costs.
Greater tolerance for imperfection may also allow simpler mounting, manual alignment of single rails, and use of standard components- further reducing costs. Lower-precision options may, however, contribute to higher maintenance costs and less durability in the future.
As such, the X-type arrangement is ideal for automation applications requiring less accuracy on assembly height and width tolerances, between +/-40μm and +/-100μm, such as packaging equipment, food processing equipment and medical sample handling.
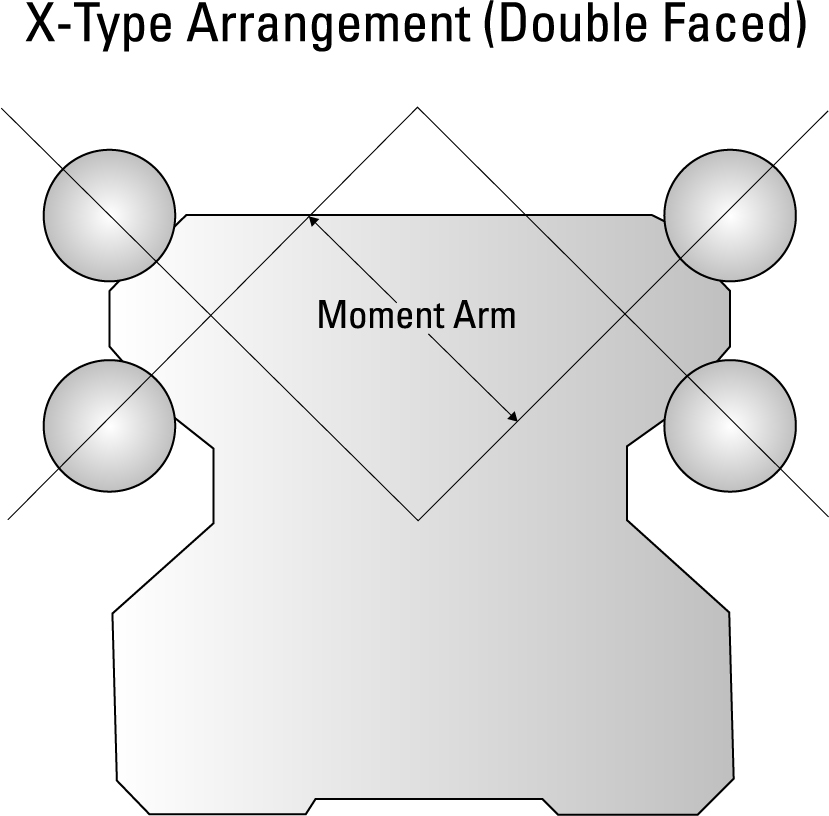
Figure 1. The X-type arrangement features double-faced ball tracks with contact angles at 45 degrees. This configuration optimizes the distribution of load across all the rolling elements.
Double-backed profile rails
All else being equal, double-backed profile rails have a higher resistance to moment loads. This is because the O-type arrangement of vectors resisting the moment load is further from the center of rotation (Figure 2), giving them extremely high rigidity and accuracy. The O-type arrangement, however, cannot tolerate misalignment or surface imperfection. Inadequate surface preparation will make the guide run rough and subject it to more frequent replacement. Even tiny flatness errors can cut reduced bearing life in half, and more severe alignment issues can result in immediate failure. These potential flaws result in a higher cost of installation, which can be several times the cost of a double-faced bearing track architecture. Typical mounting surface requirements require 15-20 times more precision than the double-faced counterparts.
Getting the necessary precision may require specialized equipment, staffing, customization, or other elaborate procedures, adding to both time and financial investment. Potential applications are those that require greater accuracy on assembly height and width tolerances, between +/-5μm and +/-50μm, such as in industrial automation, machine tool equipment, precision measuring equipment and industrial robots.
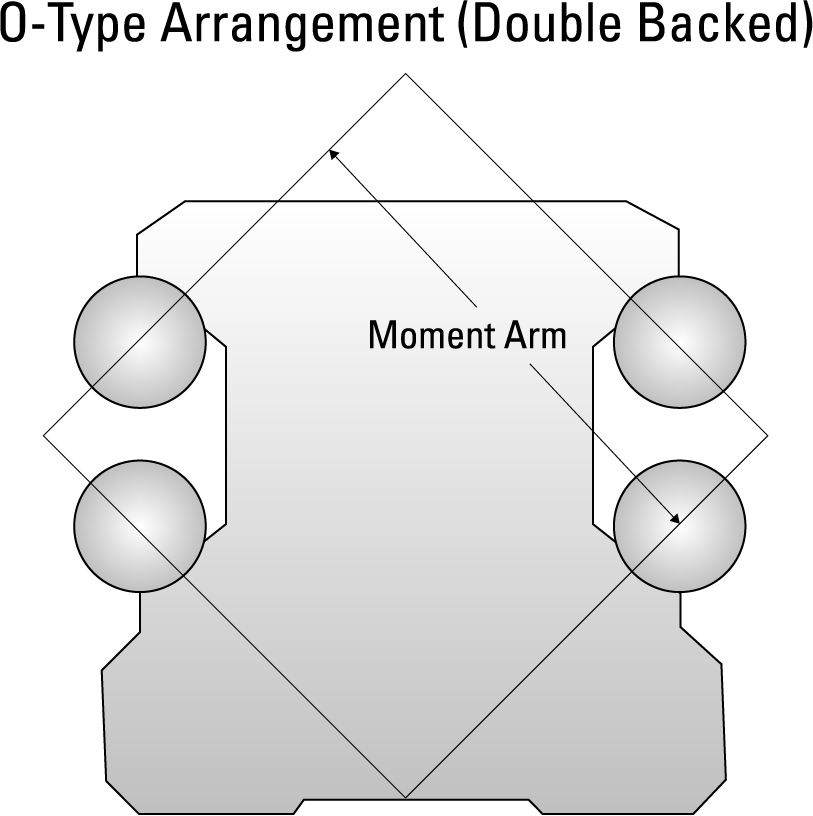
Figure 2. The O-type arrangement features double-backed profile rail further from the center of rotation for a higher resistance to moment loads. This configuration, however, cannot tolerate misalignment or surface imperfection.
Profile rail with rollers
When applications require maximum rigidity, designers may opt for rollers over balls. Rollers provide enhanced stability and load capacity with minimal rolling friction, thanks to their larger contact surface. However, profile rail with rollers also come at a higher cost and intolerance for installation variances, making them most cost effective only for the most demanding applications in terms of accuracy and moment load capacity. These include industrial automation, machine tool equipment, precision measuring and industrial robots requiring the greatest possible accuracy on assembly height and width tolerances, between +/-5μm and +/-20μm,
Managing other design trade-offs
While the selection of rail track architectures has the greatest impact on costs, other choices affecting project budgets that are within the designer’s control include material selection, maintenance, standards compliance, and training.
Material selection
Material selection can be critical in cost management, influencing both the initial and operational costs of profile rail. Aluminum offers the lowest cost but is best for lower accuracy ranges. Hardened steel strikes a better balance among cost, durability, and performance for a broader range of uses. Environments requiring high corrosion resistance or unique properties should consider stainless steel or advanced coatings, which come with a higher cost.
Maintenance
Maintenance-related decisions that can impact cost include load capacity versus size, where high load capability rails can handle heavier loads but may be larger and require more expensive and frequent maintenance. Likewise, higher accuracy demands, especially in profile rail with balls and rollers needing high speed and precision, will also involve higher maintenance costs.
Maintenance-related functions that impact cost from the designer’s perspective include the addition of features like wipers, scrapers, oil reservoirs, lube blocks, coatings, sealing and pre-loading. Whether OEMs build such functionality into their products depends on their assessment of the market demand for it.
Strategic standards compliance
Depending on location, leveraging standards strategically can help reduce costs. There are, for example, established standards for linear motion features such as rolling guides, rails and ball screws. Someone revising or rebuilding a machine in a region subject to standards that require a higher tolerance, for example, may be able to reduce cost significantly by building in a location governed by more forgiving standards, especially if the standards call for higher tolerances than the application needs.
Training
Plant managers and supervisors can also play a role in cost containment by optimizing human resources. The success of every factor discussed thus far depends on the experience and talent of the individual that is implementing it. For example, inadequate surface preparation can reduce the value of anything running on it to zero. It is up to the personnel officials to determine whether to obtain those services in-house, train teams that do not have them or bring in outside specialists. This is even more complex and critical in this age of talent shortages, where individuals may have to be trained in multiple tasks.
Conclusion
In navigating the complex decision-making process for profile rail selection, starting with a cost-effective, double-faced architecture can provide a practical baseline. From there, designers can incrementally explore more advanced options based on the specific needs of their application. By considering the broader spectrum of design trade-offs, including material choices, maintenance functionality, regulatory standards and training, designers can optimize their selections to balance upfront costs with total operational expenses.
To further assist design engineers in making the right choices, device vendors such as Thomson Industries provide design resources, including a team of application engineers who assist in identifying the optimal solution, online product selector tools, technical collateral, white papers, webinars, and video instruction.